New reality: On Saudi Arabia-Iran reconciliation and China’s role
Why in News?
Saudi Arabia and Iran, two of West Asia’s major powers that have been at odds with each other for decades, agreed to restore diplomatic relations in an agreement brokered by China.
What is the history of the ties?
- Islamic sectarianism – The rivalry between Saudi Arabia and Iran is rooted in Islamic sectarianism. While Iran is the foremost Shia state in the world, Saudi Arabia is considered to be the religious home of Sunni Islam. In modern times, this sectarian rivalry has translated into a tussle for regional hegemony. In both the wars in Yemen and Syria, Iran and Saudi Arabia find themselves on opposite sides.
- US factor – Iran is highly critical of Saudi Arabia’s closeness with the United States. The US has crippled the Iranian economy with its sanctions regime for decades.
- Militancy – Saudi Arabia is worried about the large network of armed militias across West Asia that Iran funds and backs, a threat to its own sovereignty as well as the regional balance of power.
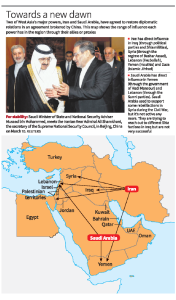
What is the agreement about?
Iran and Saudi Arabia will patch up a 7-year split by reviving a security cooperation pact, reopening embassies in each other’s countries, and resuming trade, investment and cultural accords.
Why was the agreement signed now?
Saudi Perspective
- Vision 2030 – Regional peace will be crucial to turning Saudi Arabia into the global hub that Vision 2030 envisions.
- This has led to Saudi Arabia making concerted efforts to end long-standing conflicts with powers across the region, with the Iran deal the latest such move.
- Away from the US – Furthermore, it has also led to Saudi Arabia slowly moving away from the singular influence of the United States in its foreign policy.
While the US continues to be Saudi Arabia’s biggest military supplier, in recent years, the desert kingdom has courted various powers including Russia, China and now, Iran.
Iran Perspective
- Nuclear deal – The agreement comes as Iran accelerates its nuclear program after 2 years of failed U.S. attempts to revive a 2015 deal that aimed to stop Tehran from producing a nuclear bomb. However, a brutal sanctions regime and internal tensions have made it difficult for Iran to achieve its goals.
- Regional allies –Finding allies in the region is of utmost importance to Iran when the Khomeini regime is perhaps at its weakest since the revolution.
What is the role of China in this agreement?
- China’s role as a peace broker is yet another sign of changing currents in the region.
- China has historically maintained ties with both countries and the latest deal points to China’s growing political and economic clout in the region.
What are the concerns for the United States?
- The United States has for a long time wielded great influence in West Asia.
- It has been the predominant global power that has had influence over geopolitics in the conflict-ridden region.
- Crucially, this deal and China brokering it does not portend well for the United States.
What is the impact of the agreement on other stakeholders in West Asia?
- Israel –The move has ushered in a wave of anxiety in Israel which shares no formal diplomatic ties with either nation. While Israeli leaders see Iran as an enemy and an existential threat, they consider Saudi Arabia a potential partner.
- Yemen –Riyadh intervened in Yemen against the Houthi movement after the Iran-aligned group ousted the internationally recognized government from power. Restored ties between Riyadh and Tehran could facilitate an agreement between Saudi and the Houthis.
- Syria –Iran has offered military, economic and diplomatic support to President Bashar al-Assad since his crackdown on protests in 2011 left him isolated. The Saudi-Iranian deal comes as a step towards Syria’s return to the Arab League.
- Lebanon –Lebanese politics have been broadly split for years between a pro-Iran alliance led by the powerful armed group Hezbollah and a pro-Saudi coalition. The agreement between Tehran and Riyadh has sparked hope that paralysis could end.
- Iraq –After the toppling of Saddam Hussein, Iran deepened its political, security and economic influence in Iraq, sparking Saudi alarm. Iraqis hope for a general regional detente that would allow their country to rebuild.
Way Forward
- The agreement is welcome in the context of the human toll that the Saudi-Iran rivalry has taken.
- However, this does not mean that all problems will be immediately resolved.
- While Iran and Saudi Arabia may still fall out, for the time being, this diplomatic agreement has ushered in major changes in geopolitical dynamics in West Asia.
- The agreement could be the start of a greater global geopolitical realignment.
- The announcement could not only lead to a major realignment in West Asia, but it also poses a major geopolitical threat to the United States, with China acting as a peace broker for the historic deal.
