PRELIMS BOOSTER
- Gulf Stream :
- It is a swift and warm ocean current that flows along the eastern coast of North America and crosses the Atlantic Ocean towards Europe.
- This extension towards Europe is known as the North Atlantic drift.
- The Gulf Stream transports more water than all the world’s rivers combined.
Key characteristics:
- Location: It originates in the Gulf of Mexico. It then travels northward along the eastern coast of the United States. It follows a north-eastward path across the western North Atlantic Ocean.
- Sources: The two equatorial sources of the Gulf Stream are the North Equatorial Current (NEC), which flows generally westward along the Tropic of Cancer, and the South Equatorial Current (SEC), which flows westward from southwestern Africa to South America and then northward to the Caribbean Sea. Together, these two warm currents, along with waters from the Gulf of Mexico, form the Gulf Stream.
- Warmth: The current carries warm water from the tropics (around 25 to 28°C or 77 to 82°F) to higher latitudes.
- Width and Speed: The Gulf Stream is several hundred kilometres wide and can flow at an average speed of about four miles per hour (6.4 kilometres per hour). However, its speed can vary depending on the location and other factors.
- Depth: The current is also very deep, extending to depths of up to 1,000 metres.
- Coal Gasification:
- It is the process of producing syngas, a mixture consisting primarily of carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and water vapour (H2O) – from coal and water, air and/or oxygen.
- Gasification occurs in a gasifier, generally a high temperature/pressure vessel where oxygen and steam are directly contacted with the coal or other feed material causing a series of chemical reactions to occur that convert the feed to syngas and ash/slag.
- Syngas can be used for electricity production, used in energy-efficient fuel cell technology, or as chemical “building blocks” for industrial purposes. The hydrogen can also be extracted for use in fuelling a hydrogen economy.
Benefits of coal Gasification
- Coal gasification can help address local pollution problems.
- It is considered a cleaner option compared to the burning of coal.
- It will help in reducing reliance on imports of natural gas, methanol, ammonia and other essential products.
- This holds the potential to alleviate the environmental burden by reducing carbon emissions and fostering sustainable practices, contributing to India’s global commitments towards a greener future.
- Diphtheria:
- It is a serious contagious bacterial infection of the nose and throat.
- Cause: It is caused by strains of bacteria called Corynebacterium diphtheriae that make a toxin.
- Transmission: It can spread from person to person, usually through respiratory droplets, like from coughing or sneezing.
- People can also get sick from touching infected open sores or ulcers.
- The bacteria can also infect the skin, causing open sores or ulcers. However, diphtheria skin infections rarely result in severe disease.
- Although diphtheria can be treated with medications, in advanced stages, the bacterial infection can damage the heart, kidneys and nervous system.
- Symptoms: A thick, grey membrane covering the throat and tonsils, sore throat and hoarseness, swollen glands (enlarged lymph nodes) in the neck difficulty breathing etc.
The current treatments include:
- neutralisation of unbound toxin with Diphtheria Antitoxin (DAT)
- antibiotics to prevent further bacterial growth;
- monitoring and supportive care to prevent and treat complications, e.g. airway obstruction, and myocarditis.
What are the new recommendations of WHO?
- In patients with suspected or confirmed diphtheria, WHO recommends using macrolide antibiotics (azithromycin, erythromycin) in preference to penicillin antibiotics.
- In patients with suspected or confirmed diphtheria, WHO recommends not to perform routine sensitivity testing prior to administration of diphtheria antitoxin (DAT).
- In patients with suspected or confirmed symptomatic diphtheria, WHO suggests an escalating dosing regimen for diphtheria antitoxin (DAT) which is based on disease severity and time since symptom onset, in comparison with a fixed dose for all patients.
Places in News
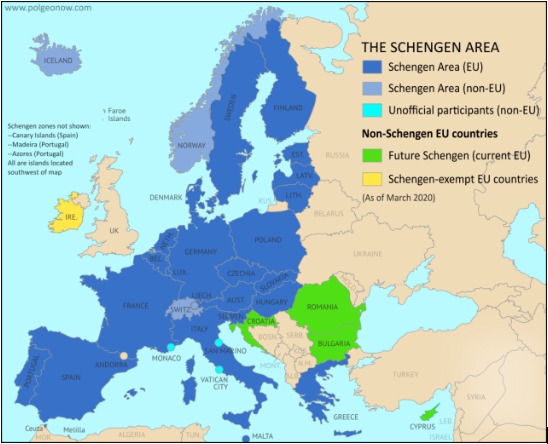
- The Schengen Zone in Europe :
- Kosovo recently secured visa-free access to the Schengen zone in Europe, world’s largest zone of free movement, becoming the last western Balkan non-European Union (EU) nation to waive visa requirements.
- Citizens of Kosovo can now enter the Schengen as tourists for 90 days within 180 days.
- The zone is known after Schengen, the tiny Luxembourg village bordering France and Germany, where the agreement was signed in 1985 among five of the six EU founding members except Italy.
- Currently, it is an area encompassing 27 European countries that have officially abolished border controls at their mutual borders.
- It mostly functions as a single jurisdiction under a common visa policy for international travel purposes.
- Croatia, a EU member since 2013, joined Schengen in 2023, while Romania and Bulgaria, EU members since 2007, will gain partial Schengen entry from 31 March 2024.