1) India EU Trade and Technology Council (TTC): Ahead of India EU TTC meeting, both have signed a MoU on semiconductors that covers cooperation in areas such as research and innovation, talent development, partnerships and exchange of market information.
- EU and India have set up TTC as a coordination platform to address key trade, trusted technology and security challenges.
- It acts as key forum to deepen the strategic partnership on trade and technology between two partners.
- It was launched in 2022 and first meet was held in May 2023
2) National Cadet Corps (NCC): NCC celebrated its 75th Anniversary on November 26.
- NCC (HQ: New Delhi) is a voluntary organization which recruits cadets from high schools, colleges and Universities all over India.
- It is largest uniformed youth organisation in world formed with NCC Act of 1948.
- Aim: To develop qualities of character, courage, secular outlook, ideals of selfless service etc. among the youth to make them useful citizen.
- Ministry: Ministry of Defence.
- Motto of NCC: Unity and Discipline.
3) National Oil Spill Disaster Contingency Plan (NOSDCP): Director General of Indian Coast Guard (ICG) chaired 25th meeting of NOSDCP in Gujarat’s Vadinar coast.
- NOSDCP promulgated by ICG (part of Ministry of Defence) in 1996.
- It is the apex plan for responding to oil spill disasters in Indian waters and is applicable to shipping, ports, and oil industries.
- ICG is Central Coordinating Authority in India for matters related to Oil Spill.
- Since 2003, NOSDCP has come under purview of National Disaster Management Authority, Ministry of Home Affairs.
- NOSDCP Objective: To establish
- Effective system for detection and reporting of spills;
- Record-keeping procedures to facilitate recovery of costs; etc
4) Social cost of carbon: According to a recent study extreme weather events can impede economic development over long term and raise Social Cost of Carbon (SCC).
- SCC is the cost of the damages created by one extra ton of carbon dioxide emissions.
- SCC helps reveal how much society should sacrifice to avoid climate change.
- Policymakers use SCC to quantify additional costs from carbon emissions not reflected in market prices.
- SCC aids cost-benefit analysis of a policy and set the initial level of a domestic carbon pricing policy
Places in News:
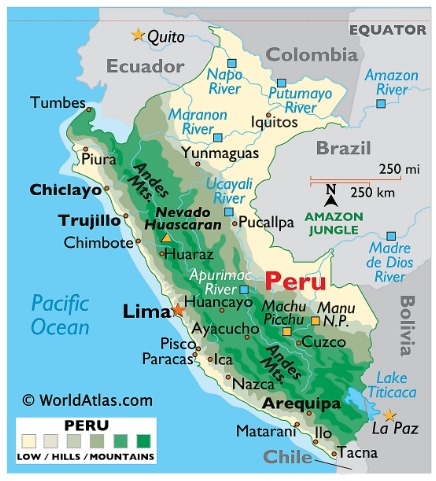
1) Peru (Capital: Lima):
- Peru has lost more than half of its glacier surface in last six decades.
- Political Boundaries
- Country in western South America.
- Bounded with Colombia (northeast), Brazil (east), Bolivia (southeast), Chile (south) and Ecuador (northwest).
- To west, territorial waters into Pacific Ocean are claimed by Peru.
- Geographical features
- Mountain range: Andes.
- Highest point: Mount Huascarán.
- Major Rivers: Amazon, Purus, Jurua etc.
- Major lake: Lake Titicaca (between Peru and Bolivia).