(GS2)
The term diaspora traces its roots to the Greek diaspeiro, which means dispersion. The Indian diaspora has grown manifold since the first batch of Indians were taken to counties in the eastern pacific and the Caribbean islands under the ‘Girmitiya’ arrangement as indentured labourers.
Recently, the Prime Minister inaugurated the 17th Pravasi Bharatiya Diwas convention in Madhya Pradesh on the occasion of Pravasi Bhartiya Diwas (PBD).
Classification:
- Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs):
- PIO refers to a foreign citizen (except a national of Pakistan, Afghanistan Bangladesh, China, Iran, Bhutan, Sri Lanka and Nepal) who:
- At any time held an Indian passport, or who or either of their parents/ grandparents/great grandparents was born and permanently resided in India as defined in the Government of India Act, 1935 or who is a spouse of a citizen of India or a PIO.
- The PIO category was abolished in 2015 and merged with the OCI category.
2. Non-Resident Indians (NRI):
- NRIs are Indians who are residents of foreign countries. A person is considered NRI if:
- She/he is not in India for 182 days or more during the financial year Or;
- If he/she is in India for less than 365 days during the 4 years preceding that year and less than 60 days in that year.
3. Overseas Citizens of India (OCIs):
- An OCI card was given to a foreign national:
- Who was eligible to be a citizen of India on January 26, 1950
- Was a citizen of India on or at any time after January 26, 1950 or belonged to a territory that became part of India after August 15, 1947.
- Minor children of such individuals, except those who were a citizen of Pakistan or Bangladesh, were also eligible for OCI cards.
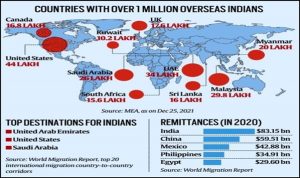
The opportunities that Indian diaspora brings for India are as follows.
- They serve as an important ‘bridge’ to access knowledge, expertise, resources and markets for the development of the country of origin with the rest of the world.
- Indian Diaspora is an important part of India’s “soft diplomacy” or “diaspora diplomacy”. For example, Indian Diaspora played a critical in the fructification of Indo-US Nuclear deal.
- They have also contributed to the growth and development of the country of their residence. For example, Silicon Valley represents the success of Indians.
- Trans-national entrepreneurship: They are a significant source of trade and investment in India.
- Source of large inflows of remittances, which has been helping balance the current account. It further aids in socio-economic development and poverty reduction.
- Diffusion of experience and exposure: They spread the Indian Culture and traditions abroad benefitting India in general. Example: Yoga, Ayurveda, Indian Cuisine etc.
- NRI’s also finance educational institutions or businesses, which again adds to the economy’s sectors. Reports suggest that these NRI’s are a major source of Foreign Direct Investment, Market Development (Outsourcing) and technology transfer, that boost the assets of the fiscal system, every day.
